Taking Service Delivery to the Next Level
What is Service Delivery?
Service delivery refers to the end-to-end process of providing services to customers, encompassing everything from receiving an order to service activation, ongoing customer support, and eventual decommissioning.
In cloud & communications industries (telecommunications, data center, SaaS, etc.), however, service delivery typically focuses on a more specific phase — covering the journey from receiving a purchase order to the service’s activation, often referred to as “turn-up.”
Also, cloud & communications providers often distinguish between service delivery, which includes initial setup and activation, and service assurance, which deals with ongoing support, issue resolution, uptime monitoring, and overall service reliability.
The Importance of Service Delivery Experience
Service delivery is the first customer experience after a purchase, and it sets the tone for the future. In the world of cloud & communications services, only support experience is more important to the users.
A smooth service delivery usually goes unnoticed, but problems in the process can do a lot of damage affecting not only customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores but also future revenue.
Service Delivery Challenges
Cloud and communications service delivery managers face several key business challenges:
- Rising expectations in terms of delivery speed/shorter intervals and customer experience.
- Increasing efficiency defined as cost per $ of MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue) turned up.
- Ability to scale and handle varying order workloads.
- Prioritize orders to turn up consistent MRR amounts.
- Ability to improve across a broad product portfolio.
At the same time, they are challenged by a rapidly evolving technology landscape, where:
- Not all services can be delivered on-demand or with a fully automated delivery.
- Exceptions disrupting regular delivery flow are frequent (no serviceability, construction required, order errors, no hardware on-stock, no capacity, etc.).
- Third-party vendors have various processes/technologies that need to be interfaced with and accommodated in the delivery process.
- Different products have different delivery intervals and workflows (e.g., Internet access vs. SD-WAN, physical vs. virtual server, etc.).
To achieve successful service delivery, providers must build systems and processes that reconcile business requirements with the complexities of vendor relationships and the underlying technology infrastructure.
Measuring Service Delivery Success
The following are the most important service delivery KPIs:
Internally measured:
- Speed: Average delivery time / interval (the shorter, the better).
- Consistency: Variation of expected vs. actual delivery intervals (lower variation indicates consistency in the process).
- Volume: Total MRR volume delivered (usually measured monthly).
- Delivery Cost: Cost per $ of MRR turned-up.
- Error Rate: The number of errors relative to order volumes or MRR delivered.
Customer measured:
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Transactional feedback, measured after each delivery.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Non-transactional measure of customer loyalty, measured at specific intervals, e.g., through a customer portal.
- Customer Sentiment Score: An AI-driven analysis of customer comments and feedback related to orders, providing deeper insights into overall sentiment.
Key Service Delivery Improvements
The following are key service delivery improvements that can be implemented within IT systems:
Automated Deal-to-Order
Problems can start before the service delivery process begins – with an order itself. Ensuring that the order is correct, and that what a customer wanted to order is what is passed to service delivery is critical: errors at this stage have a high impact on customer satisfaction, are costly to sort out, and cause significant delivery delays.
To ensure a seamless process from the systems perspective:
- Transition between a closed-won deal / opportunity in the CRM / CPQ to service delivery must be automated, and ideally, triggered by customer signature.
- Automation must support complex, multi-line orders.
- Quote-to-order must support service changes such as Moves, Adds, Changes and Disconnects (MACDs).
Automated Order Processing Kickoff
Providers with complicated product portfolios and complex (e.g., large enterprise or wholesale) orders employ an order validation process before passing them down to service delivery.
The validation process is often manual and may cause unnecessary delays if an order is missed. Automated assignment to orders person along with a notification can mitigate the problem.
Additional efficiencies can be gained by routing orders automatically to team members based on their availability, workloads, and skill sets. For example, Nextian Order Management can use process flows or Salesforce Omni-Channel to implement intelligent order routing.
Task Automation
Service delivery process consists of multiple, inter-dependent tasks.
In the ideal world, the delivery process would be 100% automated (“zero touch provisioning”); however, in reality, some tasks can be automated, while others cannot. The potential level of automation is highly dependent on the product (e.g., a virtual machine is easy to spin up, Internet access product setup involving a third-party provider is much more difficult to automate).
Automating as many tasks as possible and reducing the number of manual order touches in the service delivery are paramount to achieving maximum efficiency.
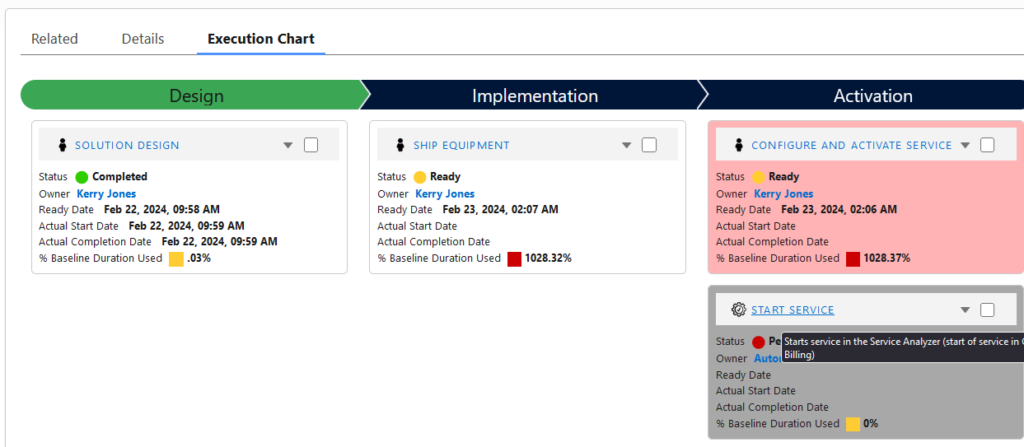
Intelligent Task Assignments
Depending on provider size, any given time there may be hundreds of manual tasks ready for execution, spanning multiple orders, order types (service turn up/change/disconnect), products, underlying vendors, turning task assignments into a nightmare for service delivery managers.
While the manual tasks themselves cannot be automated, their assignments can. Automated task assignments can be driven off:
- Type of task, product, order, customer,
- Employee availability,
- Current employee workloads,
- Employee skills and other factors.
For example, Nextian Order Management can use process flows or Salesforce Omni-Channel to implement intelligent task routing, freeing managers’ time and ensuring that work is assigned in a timely manner.
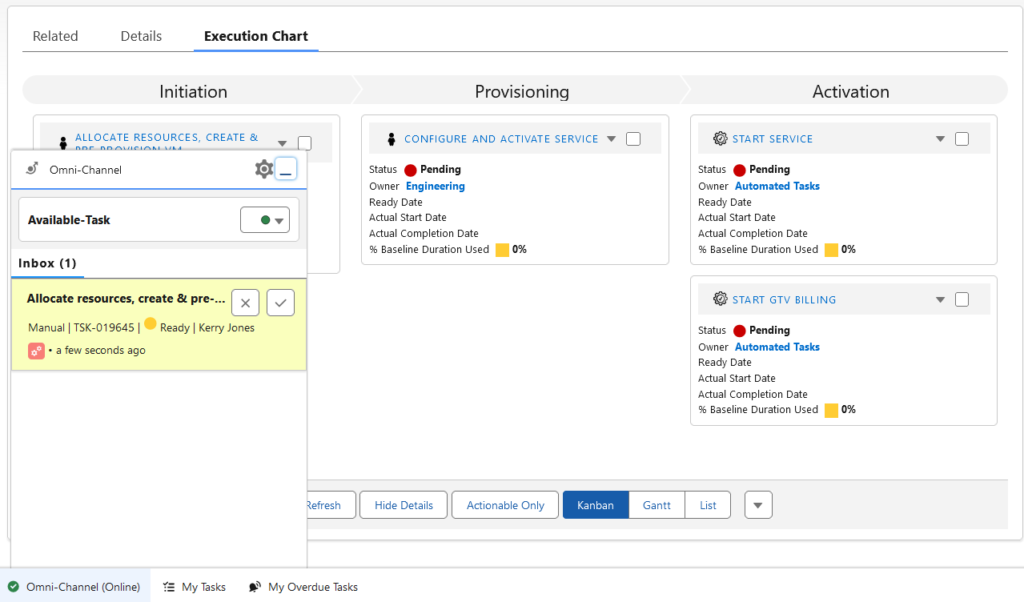
Automated Status Reporting and Forecasting
Preparing status reports and establishing service Projected Installation Dates (PIDs) can be a time-consuming activity for service delivery managers. This is especially true for providers dealing with large volumes of smaller orders that still require modifying the hardware infrastructure (e.g., broadband Internet, physical servers).
To ensure accuracy, forecasting should be automated and accessible internally for the service delivery teams as well as (in a limited fashion) for customers in the customer portal.
Nextian Order Management fully automates the forecasting process, adjusting delivery dates every time a task is completed, and daily for orders that are not moving. Order status and delivery forecasts are also available in the Customer and Partner portals.
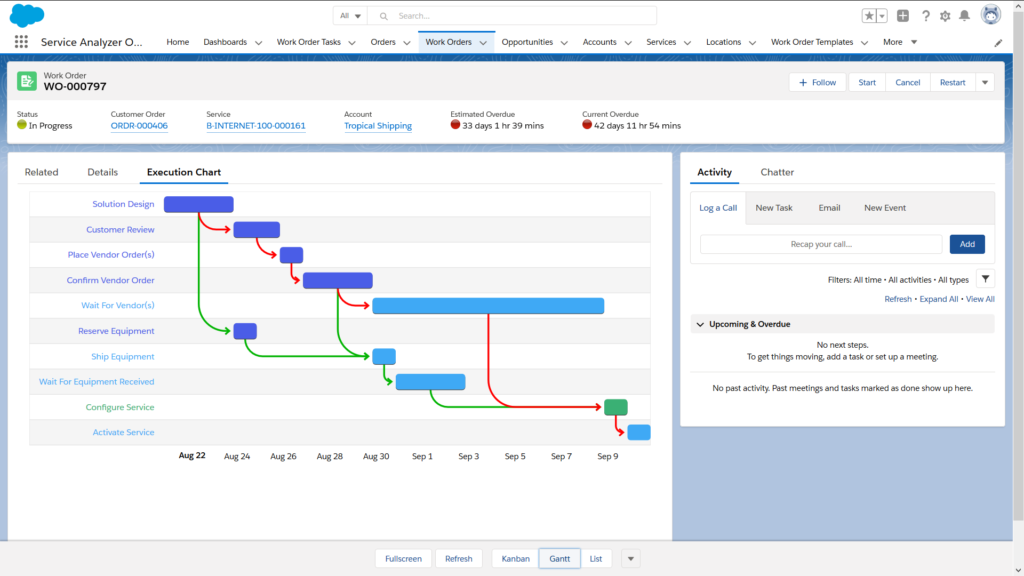
Effective Communication
Effective communication, both internally as well as with customers and partners, is essential to ensure seamless delivery and high CSAT scores. It is especially important for large enterprise deals (such as multi-site, multi-data center or region, multi-service deployments) involving a lot of moving parts.
Communication can be improved with email notifications, chatter updates, task alerts as well as with order status updates in the customer portal.
Bi-directional communication, so that customers can post comments and upload files (rather than just consume information) drives additional efficiencies and reduces communication overhead.
Risk Management
Managing risks (also referred to as jeopardies) is an underrated aspect of service delivery.
However, risk management is essential for managing customer expectations and (perhaps more importantly) enable measurements allowing service delivery process improvements, identifying:
- Products that cause most trouble to deliver (in numbers but also in affected MRR),
- Steps in the process causing issues,
- Classes of problems (so they can be addressed one by one).
Used in conjunction with customer portals, risk records can be an excellent means of requesting information from customers.
A good risk management process builds customer confidence in provider (issues identified & addressed quickly, provider has a good handle on the delivery process, etc.) leading to high CSAT scores.
Accurate Financial Reporting and Forecasting
Making forward-looking financial projections based on high volumes of in-progress orders of all kinds (new services, changes, disconnects) with ever-changing delivery schedules can be quite challenging.
However accurate service delivery financial forecasts (such as new revenue billed in upcoming months) are required to effectively run the business.
Nextian orders combine forecast and financial information feeding Nextian Business Analytics module providing finance and service delivery managers with up-to-date information in real-time.
Improving Service Delivery with Nextian Quote-to-Cash
Order Management is a primary module handling ordering and service delivery within the Nextian Quote-to-Cash platform. It is integrated with other modules to provide a seamless service delivery experience:
| Module | Service Delivery Features |
|---|---|
| Order Management |
|
| Customer Portal |
|
| Partner Portal |
|
| Reporting & Analytics |
|
Conclusions
Managing service delivery across a large number of orders spanning a broad product portfolio can be a daunting task for service delivery managers. Additionally, service delivery represents the first customer experience after a purchase, making it essential to ensure the smoothest delivery possible.
A good order management and service delivery software plays a critical role in optimizing the process, and ensuring that:
- Delivery timelines and intervals are consistently met.
- Performance metrics are accurately measured and reported.
- Delivery costs per dollar of MRR remain low.
- Error rates are minimized to improve efficiency.
- Risks are effectively managed, communicated, and quickly resolved.
- Progress is tracked and communicated transparently — internally, to customers, and if applicable, to partners.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS) remain high and consistent.
Nextian offers products and services that help cloud and communications providers streamline their Quote-to-Cash and service delivery, driving revenue growth and customer retention.
Contact us today to find out how we can help you!