Top Tools for Effective Salesforce Development
Salesforce offers basic development tools — Object Manager and Developer Console — built into every instance (or an “org” in Salesforce nomenclature). These are typically sufficient for maintaining a small CRM org with minor customizations like adding fields, validation rules or modifying layouts.
However, organizations that take full advantage of Salesforce with a lot of customizations and development (custom objects, developing APEX code, VisualForce pages, Lightning Components, integrations and others) require a more robust toolset.
Good tools are not just a convenience for developers — they can lead to substantial savings through faster development, improved code quality and reduced user-downtime.
Over a few years of development at Nextian we’ve experimented with many development tools and would like to share which worked best for us.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
The choice of IDE is one of the most important ones, as this is where developers will spend most of their time. As of writing of this post, IntelliJ IDEA (Community Edition) with Illuminated Cloud plugin is our #1 choice. While the first one is free of charge, the other one is a subscription offering. Together they enable:
- SOQL query completion with concurrent connections to multiple orgs
- APEX with code completion (both anonymous and for writing classes) and syntax highlighting
- Step through-debugging
- Running tests from the IDE
- File deployments from the IDE
- Static code inspection
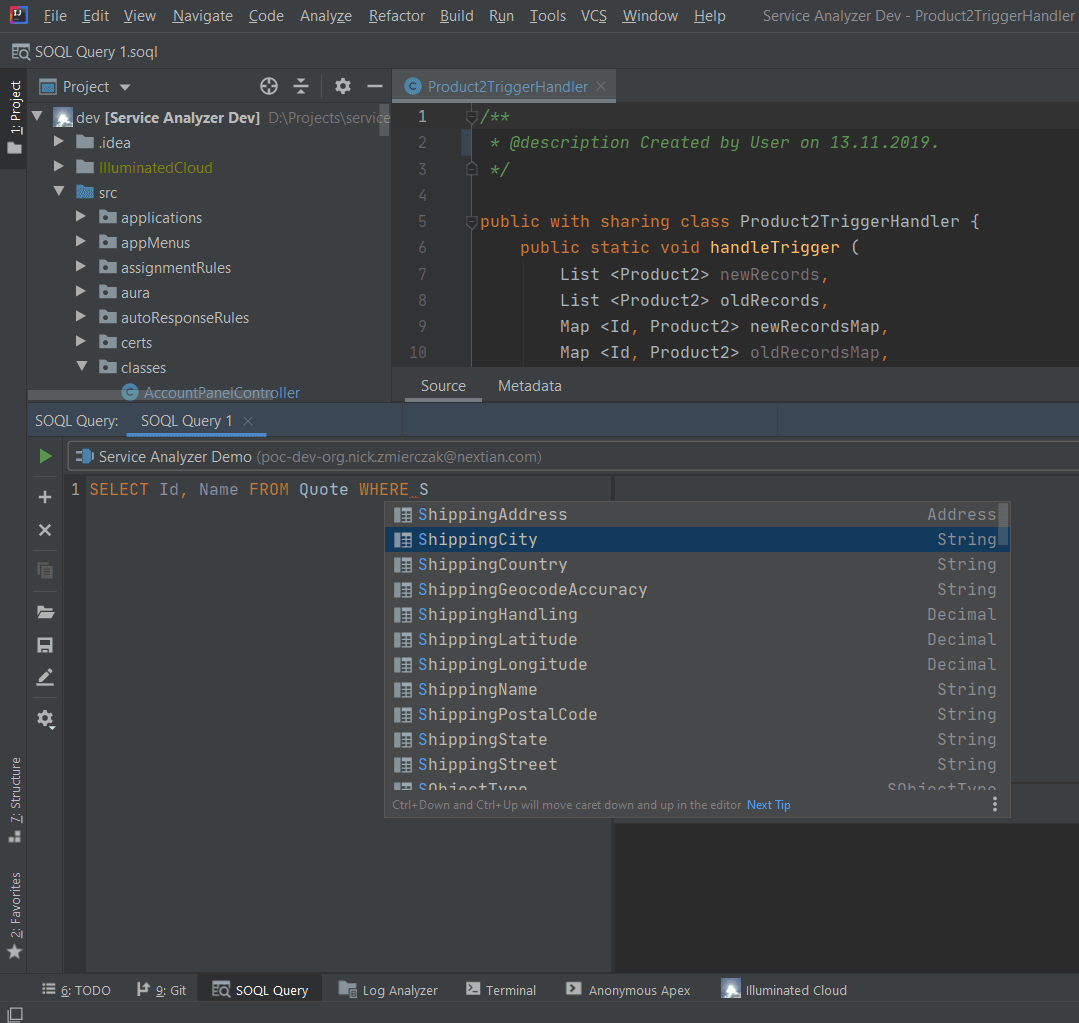
Maven Tools for Chrome is a free Google Chrome extension mimicking a simple IDE featuring an intelligent SOQL query editor, APEX code editor, object inspector, deployment tools, log browser and others. While not a replacement for a fully-blown IDE, it is a useful tool for troubleshooting, data migrations and small deployments.
Static Code Analysis
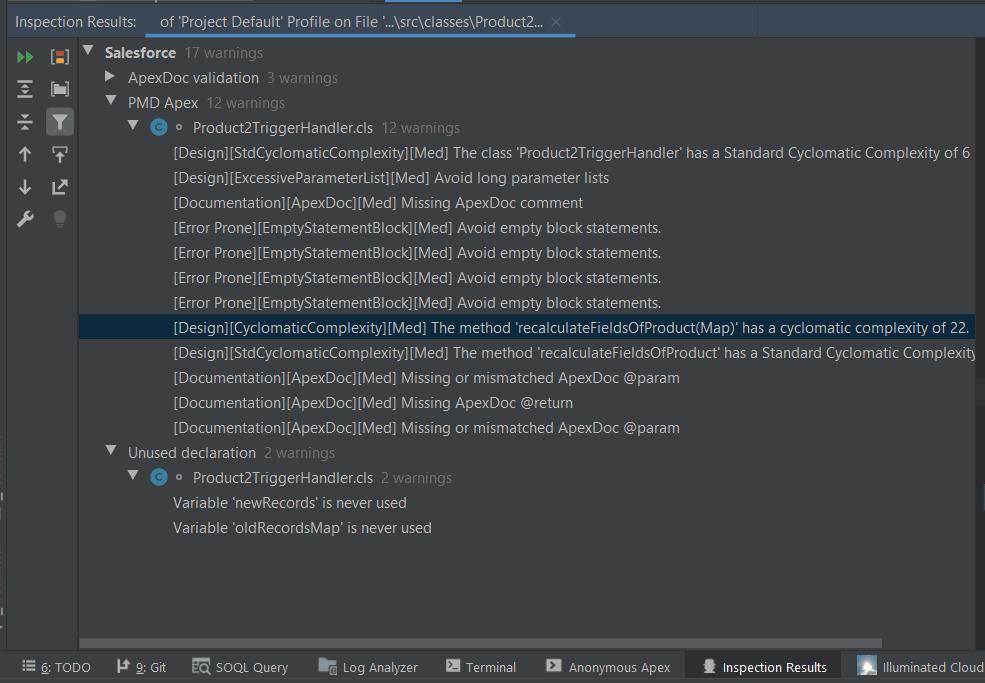
While the IDEA/Illuminated Cloud tandem offers good code analysis, it can be further enhanced by using PMD APEX (running from IDEA).
Static code analysis improves software quality and becomes especially important when building packages for AppExchange: PMD APEX can substantially reduce time spent passing scrutiny of the Force.com code scanner and Salesforce engineers.
Backup
Backup tools not only give recovery capability, but also help developers with:
- Tracking metadata changes with diff comparisons and email alerts. This comes particularly handy if users apply changes on production without letting the development team know.
- Moving data (seeding) between orgs (e.g., copying production data to test sandboxes). This enables overcoming full sandbox limitations on refresh frequency, or getting rid of them altogether.
- Anonymizing data — useful when working with an outsourcing partner to limit access to live data, or to anonymize phone numbers or emails so real customer data is not used in automated process flows.
An overview of Salesforce backup tools is provided here.
Development Sandboxes
Just like in case of development in any other programming language, separate environments for development, production and testing are a must.
Salesforce offers additional separate orgs (“sandboxes”) of four types that can be purchased with a subscription: Developer, Developer Pro, Partial Sandbox and Full Sandbox (they can be managed via Setup → Environments → Sandboxes). The first two can be used for development, the latter two for testing.
A full sandbox is a 100% clone of production and can be especially useful for data migrations or testing on large sets of production data. It has some limitations though: it’s pretty expensive and has a limit on refresh frequency (30 days). A good backup tool can be used to refresh data more often.
Source Code Management (SCM)
Metadata is the “source code” for Salesforce. Since it is a collection of text files, it can be tracked in virtually any source code management system. Since we use Atlassian JIRA internally at Nextian we settled on Bitbucket with the Git front-end managed via SourceTree or IntelliJ IDEA. There is however plenty of choice: we’ve seen projects on GitHub and Microsoft VSTS as well.
| Important | The exchange of metadata files takes place between Salesforce and IntelliJ (a local filesystem). Therefore, the ultimate source of truth for metadata is Salesforce not the filesystem, but the SCM works off the later. This can lead to problems with many developers pushing changes in parallel. |
For this reason, we recommend designating a single team member to push the code to the SCM.
Build and Deployment Automation
Access to Salesforce metadata is provided by the Metadata API.
Salesforce CLI (a.k.a. SFDXCLI) is a metadata API command line tool provided by Salesforce enabling:
- Pulling sources (metadata) from orgs.
- Creating and managing new orgs.
- Pushing code to specified orgs.
- Executing tests.
- Creating and installing packages.
Coupled with scripting and batch jobs, SDFDXCLI can be used to automate build, test, deploy cycle and run DevOps on Salesforce.
Web Browser Add-ons
Standard web development tools for JavaScript debugging & profiling come very handy for Lightning component development.
Also, a number of add-ons such as Better Formula Editor exist for improved syntax highlighting and auto-complete for Salesforce formulas.
Maven Tools for Chrome is an excellent, free Google Chrome extension for working with SOQL, APEX, objects and others from within the browser.
Test Case Management
Salesforce unit tests and coverage requirements help to improve quality, however in most cases they will have to be augmented by external, manual or automated test cases.
At Nextian we use QMetry for JIRA to track and execute manual test cases & plans (XRay is also a good package, however as of this writing it does not support JIRA next gen projects that we use).
| Important | It is a good practice to capture test cases along-with developing software functionality: ask developers to capture basic test case scenarios, so QA can provide the details and expand later on. |
Lightning Components Debug Mode
Debug mode is useful when developing custom components for the Salesforce Lightning Experience in JavaScript.

It disables caching and provides additional information to developers in the browser console.
To enable Lightning debug mode, go to:
Setup → Custom Code → Lightning Components → Debug Mode
Conclusions
A robust development toolset is important for productivity, code quality and easy deployments. From the business perspective, it can enable substantial savings through quicker development, lower cost of maintenance and shorter downtimes affecting the users.
While Salesforce development tools may not be as sophisticated as those for traditional programming languages like Java or Python, the tools described can still significantly benefit Salesforce development teams.
Contact us today to find out how we can help you!






