CPQ and Quote-to-Cash – a five-minute overview

Today’s marketplace offers abundance of products and services for Quote-to-Cash (QTC or QTC) and Configure, Price, Quote (CPQ).
With the multitude of offerings (including Nextian), potential buyers struggle to navigate this complex space.
The objective of this post is to clarify the terms, concepts and elements / building blocks of QTC and CPQ in an easy to understand, five-minute overview.
CPQ vs. QTC
While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they mean two distinct things:
While CPQ is usually associated and implemented within CRM systems, this does not have to be the case.
QTC is a larger continuum encompassing activities from sales, through order processing & fulfillment, all the way to billing and collections (i.e., from deal origination until the payment has been received) — CPQ is only a part of QTC.
QTC usually spans across more systems than just CRM. For example, in the communications industry QTC would involve CRM, provisioning, billing and financial systems (read more on Wikipedia).
While CPQ may be a tactical project, QTC is a strategic activity with a broader perspective embracing multiple IT systems, architecture, transformation roadmap, etc.
Business first, systems secondQTC must be examined from the business perspective first:
IT Systems and architecture selection is secondary and can only be done once the above questions have been fully answered. See also this post with a model for establishing QTC optimization priorities. |
CPQ — Key Functions Overview
CPQ is the front-end of QTC allowing sales reps to:
- Configure: select customer-facing product offering for the quote (products, services, options, terms, etc.)
- Price: select price books, retrieve list pricing, choose quantities, apply markups and discounts
- Quote: request approval, generate quote document and obtain customer signature
While all of these seem straightforward, the following must be considered:
- Product catalog cleanup. While CPQ implementations are often focused on sales reps (who are the end-users), the project brunt is often on product management teams: cleaning up products and pricing, consolidating Excel spreadsheets, getting rid of obsolete products, reviewing SKUs, etc. These activities make up a huge chunk of any CPQ project.
- Considering additional quoting parameters (a.k.a. dimensions). Most CPQ products will do fine for quoting new widget products. The challenge arises when additional dimensions are added such as subscription term length, renewal-type, SLA commitments, etc.
- Dealing with subscriptions and operations during their lifecycle (e.g., re-term, re-rate, replace, upgrade etc.) — while they can be treated as additional dimensions, they also require current subscription information which may not be available in the CRM.
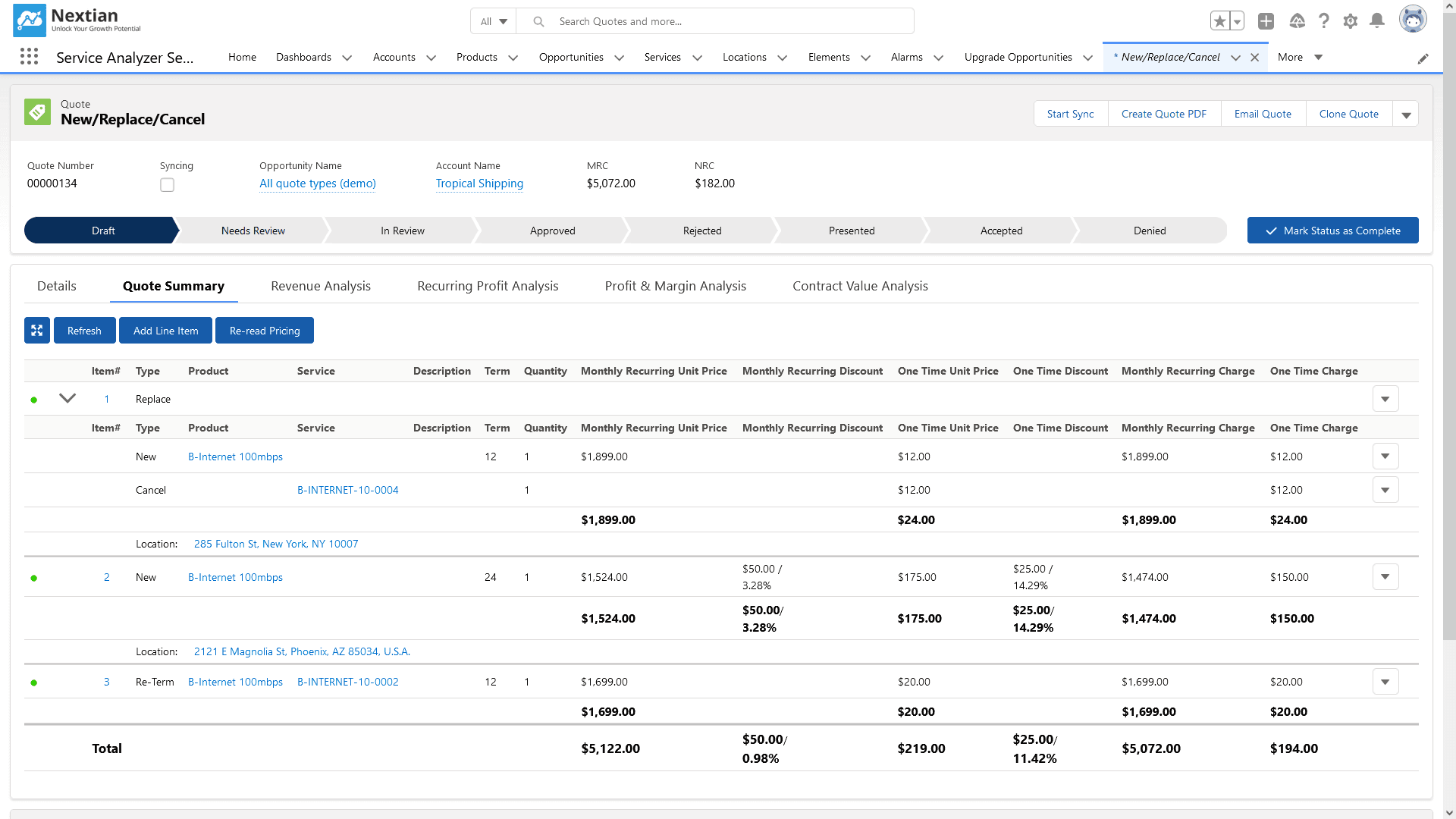
QTC — Adding More Systems
Once quoting is in place, additional pieces of the puzzle kick in:
- Contracts management — supervise customer contract life cycle for master (general T&Cs) and individual service (start of service, term, renewal) agreements.
- Order management, fulfillment & delivery — convert an ordered quote into a subscription service or product delivery.
- Customer support — ensure customer support for products (e.g., warranty for a widget depending on a date of sale) and subscriptions (availability and SLA-levels).
- Billing & invoicing — collect usage information and produce invoices.
- Payment processing — ensure that customers can pay for product and services both traditionally (mailed check) and on-line (credit card, ACH, wire transfer, etc.).
- Self-care portals — enable customer self-service.
All of these are usually complemented by ‘operational’ systems like reporting, data warehouses or domain specific ones such as network and infrastructure monitoring.
It is easy to notice that this picture may get complicated very quickly — and indeed, designing a business QTC architecture is usually a complicated undertaking.
Key Elements of QTC
All the above can be quite overwhelming. However, no matter what systems are used, QTC can be somewhat abstracted into elements that make it.
Product & Pricing
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
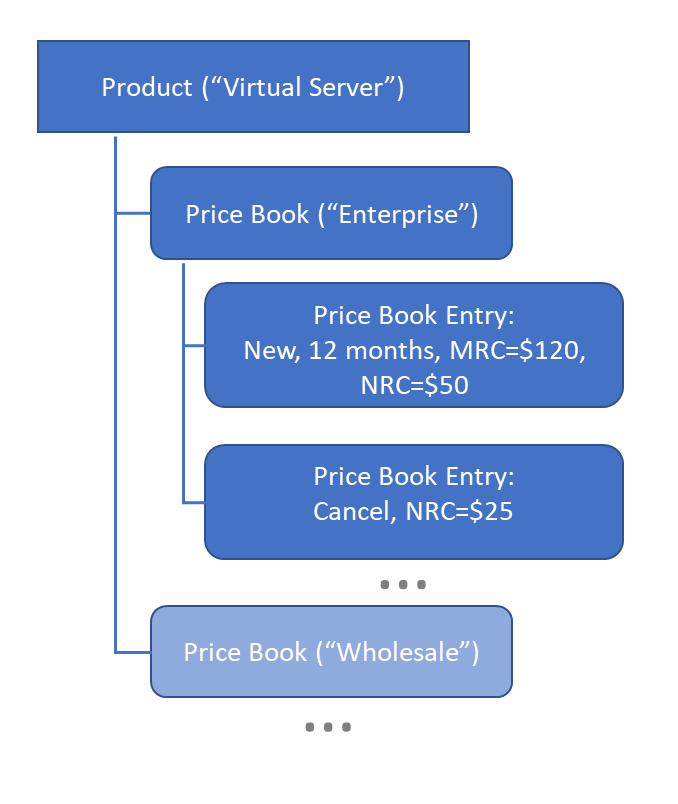
| Price Book | Price books typically correspond to particular markets such as Wholesale or Retail and define available products and their pricing for those markets. |
| Product | Represents offered products (e.g., a ’16GB Virtual Machine’, ‘Internet Access’) and their key attributes (e.g., a widget, a subscription, a part that goes with other products, product family, etc.), usually without pricing information. |
| Price Book Entry (PBE) | Determines product pricing within a price book and additional quoting parameters (a.k.a. quoting dimensions) such as term, SLA level, etc. |
The relationship between price books, products and price book entries can be visualized as follows:
Quoting and Opportunity Management
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
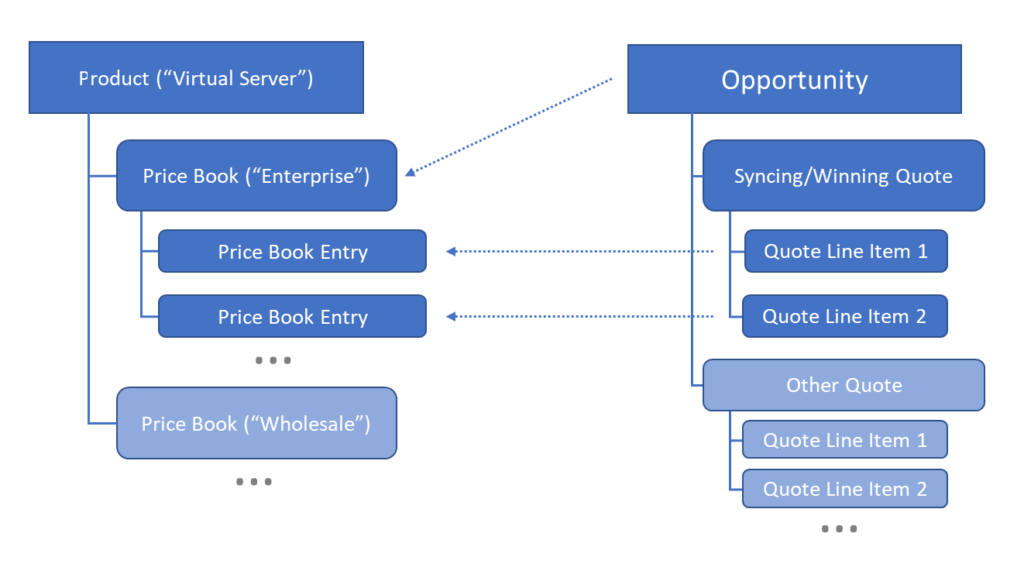
| Opportunity |
Opportunity is one of the key CRM objects — it identifies a customer request for products or services, sales numbers and win probabilities. Opportunities go through various sales stages and once the opportunity has been Closed Won, an order is created. Typically, an opportunity would allow for price book selection, and the underlying quotes would always use that price book. |
| Quote |
A quote designates a formal offer for products or services with prices, quantities and discounts — a quote document is presented and accepted by customer. A single opportunity may have multiple quotes (e.g., 12, 24 and 36 month term). |
| Syncing Quote | A syncing quote is single quote within an opportunity that is included in the sales forecast (the most likely quote to win). |
| Winning Quote | A quote that was eventually ordered by the customer. |
| Quote Line Item | Quotes consist of multiple line items, which are usually related to price book entries. |
The relationship between opportunities, quotes, quote line items and price books can be visualized as follows:
Order Management
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Order |
Orders are the main vehicle for product and service delivery:
|
| Order Line Item | Just like a quote, an order consists of one or more order line items. Typically line items relate 1:1 between order and quote. |
| Work Order |
Work orders are made of tasks (either user-executed or automated) along with their dependencies determining a sequence of actions for delivery. Typically, each line item on an order would have a corresponding work order. |
| Subscription Service | Customer subscriptions created in the process of order delivery. |
So far, the QTC process can be visualized as follows:
Integrating Billing
Up to this point (quote to subscription), the items described above are more or less common across multiple systems and CRM/CPQ vendors.
Things get complicated when billing is brought into the picture. Billing is usually a separate system.
The separation creates the following questions:
- Where does the product catalog reside?
- How is CRM/Quoting synchronized with billing?
- Where is the cut-off between CRM and billing in delivery?
CRM/BILLING SEPARATION
With CRMs providing more functionality than traditional sales tracking (CPQ, orders, support, etc.), the question is how to draw a line between CRM and billing. The following approach is recommended by Nextian:
|
Conclusions
While tactical CPQ projects are relatively easy, the challenges arise when incorporating CPQ into a larger QTC continuum.
Nextian is a vendor of Quote-to-Cash (QTC) software for cloud and communications helping providers accelerate growth and increase customer lifetime value.
Contact us today to find out how we can help you!
Related posts
2024 telecommunications industry trends in quote-to-cash
Learn about 2024 telecommunications industry trends: shift towards software, digital experience, automation, API-fication and AI & algorithms.
Increasing sales velocity for cloud & communications services
Increase sales velocity of cloud and communications services and quickly generate revenue with rapid quoting, automated renewals and omni-channel sales.
Subscription service contract renewals for cloud & communications
Learn how to leverage Nextian for automated subscription service contract renewals with a high success rate and reduced month-to-month revenues.
GET THE NEXTIAN ADVANTAGE
We help enterprises increase revenue, profitability and gain efficiencies by realizing the full potential of the Salesforce platform.




