Choosing Salesforce AI — Key Decision Factors
Integrating AI into Salesforce can significantly enhance CRM capabilities, driving better decision-making and increased automation. While Salesforce is traditionally used for sales and marketing, it can also be used in other areas such as order management and customer support. Augmenting those with AI can unlock even greater benefits.
With AI being such a hot topic, many CIOs and CTOs face the challenge of choosing the right technology. Should you opt for Salesforce’s Einstein, explore OpenAI, or consider solutions from other providers such as AWS, Google or Microsoft? Or perhaps a combination of these?
This post is designed to guide CIOs and CTOs of organizations using Salesforce through the decision-making process, helping you select the best AI solution to meet your needs.
It’s important to note that there are no universally right or wrong choices when selecting an AI provider. The best decision will depend on several factors, which are outlined below.
Available Options
When integrating AI with Salesforce, the primary options include the following providers:
- Einstein: Salesforce’s native AI platform, offering a suite of easy-to-use and configurable applications designed to enhance CRM capabilities.
- OpenAI: A leading AI service renowned for its natural language processing and generation capabilities, widely recognized for tools like ChatGPT (used at least once by 43% of adults aged 18-29 in the U.S.).
- AWS AI Services: A suite of pre-trained and customizable artificial intelligence tools from Amazon Web Services.
- Google Cloud AI: A set of machine learning and AI tools, including pre-trained models and customizable solutions to build, deploy, and scale AI-driven applications on Google Cloud’s infrastructure.
- Microsoft Azure AI: A range of AI services enabling businesses to integrate advanced AI capabilities into their applications and workflows using Microsoft’s cloud platform.
Key Considerations
The following key considerations will drive the choice of the AI provider for Salesforce:
AI Applications
Identifying the key areas where AI will be applied within the organization is, in our opinion, the most critical factor when selecting an AI provider:
- What applications will AI be used for? Will the applications be limited to straightforward tasks such as sales and marketing analytics within the CRM, which platforms like Einstein can easily handle? Or will they extend beyond traditional CRM functionalities to include areas like network analytics, fraud detection, IoT product performance, or other specialized domains?
- What are AI use cases? Will AI be used primarily for interactive or generative tasks, such as crafting customer support responses? Or do they involve complex analytics, like generating insights or detecting fraud, which involve longer, background processing cycles?
AI Users
The way end users consume AI results is as important as sourcing and processing the data. AI outputs will only deliver business value when they are accessible and actionable for users.
- Who are the primary users? Are they sales representatives looking for predefined results? Data scientists who need to delve into the data to identify patterns and answer critical business questions? Or is there a need to cater to both groups?
- Access to AIs results? Determine how users will access AI results. Will the results be available exclusively through the Salesforce user interface, or will they be integrated into other applications as well?
AI Data
Beyond basic generative AI applications like chatbots or tools that assist technicians in generating support responses, and particularly for non-interactive tasks such as generating insights, simple data queries are insufficient as inputs. This is why, in most cases, AI needs to operate in tandem with a data lake.
Given the common misconceptions about data lakes, it’s important to first clarify what a data lake is, starting with the key differences between a data lake and a data warehouse:
| Description | Purpose | Primary User |
|---|---|---|
A Data Warehouse (DWH) is a specialized database designed for analyzing “facts” (e.g., sales data) across various “dimensions” (e.g., quarters, geographic regions). The data structure — consisting of predefined facts and dimensions – is established upfront to deliver quick and efficient query results. Before data is loaded into the DWH, it typically undergoes processes like cleaning, enrichment, and transformation, ensuring it serves as the organization’s “single source of truth.” | DWHs are typically used for operational reporting and analysis. | Data analyst is the primary DWH user, analyzing data through routine analysis and creating reports. |
A Data Lake (DL) is an evolution of a data warehouse that stores both structured and unstructured data at a much larger scale. Structured data typically originates from business applications, while unstructured data can come from various sources such as networks, social media comments, IoT devices, and others, and is stored in its raw, original format (“as-is”). | Uncover insights, and patterns, answer business-related questions using SQL queries, big data analytics, full text search and AI. | Data scientist who works on new ways to capture, store, manipulate, and analyze that data. |
Introducing AI to the organization involves addressing two key challenges: selecting the right AI technology and implementing an effective data lake. From a data lake and data management perspective, the following factors need to be thoroughly analyzed:
- Data Sources and Master Data. Is AI relying solely on Salesforce data for queries and insights, or are there multiple data sources involved? How complex is the process of sourcing this data? Additionally, where is the master data for each data type located?
- Data quality. Similar to a data warehouse and its reports, the accuracy of AI-generated results depends heavily on the quality of the data provided. If the data is of poor quality, with numerous gaps and errors, it is strongly recommended to address these data quality issues before implementing a data lake.
- Data Volumes and Storage Costs. What are the anticipated data volumes that will be stored in the data lake? Does the data lake support “zero copy” functionality to prevent data duplication and reduce storage costs?
- Data Retention. What is the retention strategy for data stored in the data lake? What are data retention policies in source applications (especially for “zero copy” data)?
Security & Compliance
Data security and compliance are broad and complex topics, but from the perspective of AI and data lakes, three key issues stand out:
- Consolidated Data Security. Data lakes consolidate data from multiple sources, including sensitive information. Ensuring access data control is a challenge, especially for unstructured data.
- AI Access to Sensitive Data. AI models may use data that includes personally identifiable information (PII) or other sensitive data types. Adhering to regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA can be challenging when data is aggregated, and difficult to track back to its original source.
- Accidental Sensitive Data Exposure. AI models can unintentionally reveal sensitive data by learning patterns and gathering insights from the data that should remain confidential.
Other Factors
Beyond AI functionalities and obvious factors like cost, there are a few less apparent considerations that are also important to keep in mind:
- Ease of Integration and Development. AI integrations can vary widely, from straightforward REST API calls to more complex setups using platforms like MuleSoft and tools like SageMaker Studio. Additionally, integrating with a data lake may also be required. Each of these options comes with its own costs, complexities, and learning curves that need to be carefully evaluated when planning AI implementation.
- Current IT Environment. AI implementations do not occur in isolation; they must align with the existing IT infrastructure. For a business that primarily uses Microsoft solutions, sticking with Microsoft for AI may be the most sensible choice. Similarly, a company that operates an Oracle data warehouse and uses NetSuite for ERP might find Oracle Cloud to be the best fit. It’s important to remember that the vendor with the most advanced features isn’t always the best match from a technology compatibility standpoint.
- Vendor Diversity & Avoiding Lock-in. Vendor diversity and avoiding vendor lock-in are important because they prevent dependency on a single provider, reduce risks associated with service disruptions, and high switching costs.
Salesforce and OpenAI
API integration:
a step-by-step guide
Discover how to integrate Salesforce with the OpenAI API to harness the power of generative AI and natural language processing.
Choosing the Right Option
After reviewing all the information, considerations, and factors, the question remains: how should you decide on an AI provider for Salesforce?
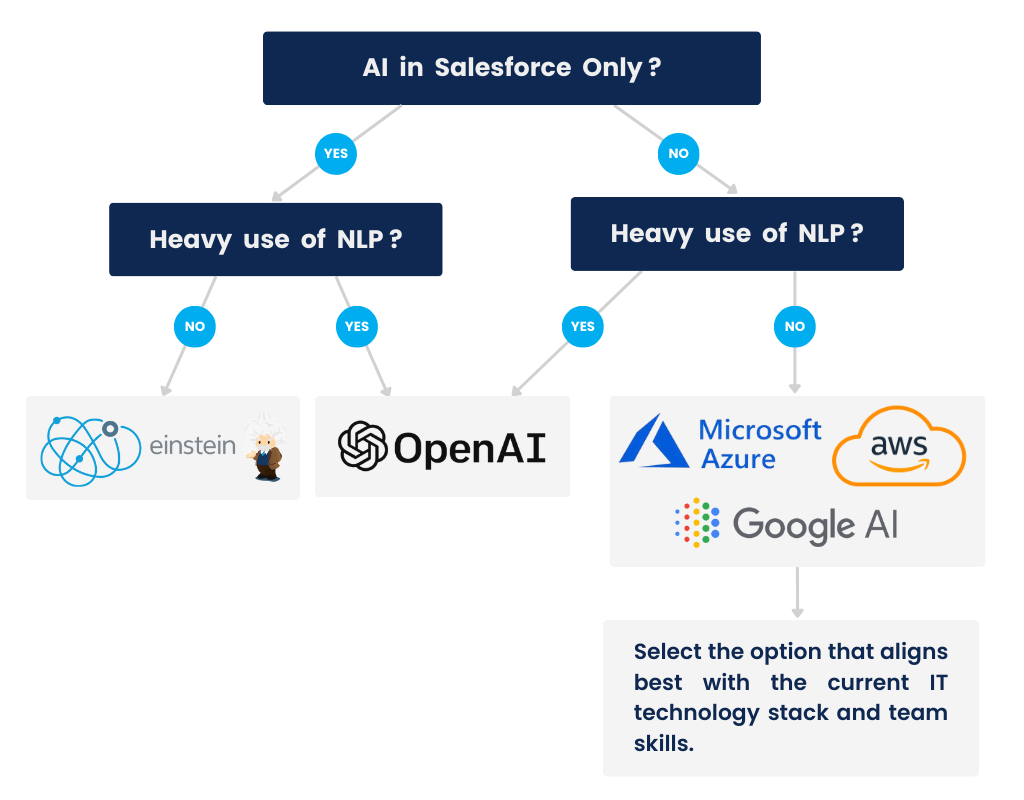
While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, here’s our recommended decision tree:
|
Decision making process can be visualized as follows:
Conclusions
AI is already transforming organizations across various sectors and will continue to do so. For organizations using Salesforce, choosing the right AI provider is not straightforward, as it depends on several factors outlined above.
The AI market is changing dynamically and will probably be different in a year from now, so any decisions made today may need to be reassessed in the future, as new advancements and possibilities emerge.
Nextian offers products and services helping businesses improve their Quote-to-Cash to drive revenue growth and customer retention. Our offerings include advanced AI solutions in the areas of customer support (generative AI, ticket routing), and analytics (sentiment scoring, churn prediction, skills-based matching), especially in conjunction with CRMs and customer support systems.
Contact us today to find out how we can help you!